一、resultMap的使用
resultMap 也是定义返回值类型,返回值为用户自定义的类型,可用于解决JavaBean中的属性名和数据库中的列名不一致的情况
之前对于JavaBean中属性名和数据库中的列名不一致的情况,通过有两种办法,1、通过在sql中使用别名 2、如果正好符合驼峰命名,需要在settings中配置,现在可以通过resultMap来解决
hotelMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.pjf.mybatis.dao.HotelMapper">
<!-- resultMap定义
type:javaBean的全类名,
id为该resultMap的唯一标识 -->
<resultMap type="com.pjf.mybatis.po.Hotel" id="myHotel">
<!--id 指定主键的封装规则
column:数据库中列名
property:javaBean的属性名 -->
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<!--result 指定非主键的封装规则
column:数据库中列名
property:javaBean的属性名 -->
<result column="hotel_name" property="hotelName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="hotel_address" property="hotelAddress"
jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="price" property="price" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
</resultMap>
<!-- resultMap使用 -->
<select id="getHotel" resultMap="myHotel">
select * from hotel
where
id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
二、association的使用
association和collection都是用来关联另一个表的数据,区别就是用来关联对象的封装的,而collection是用来关联集合封装的,
举个例子,比如通过查询酒店,查出该酒店的城市,是一个城市对应一个酒店,用association
而查询一个城市的酒店,是一对多的,用collection,下面来具体实现下这个例子。
1、环境准备
修改hotel.java代码,增加一种类成员变量City,通过查询酒店,直接查出他所在的城市
package com.pjf.mybatis.po;
public class Hotel {
private int id;
private String hotelName;
private String hotelAddress;
private int price;
private City city;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getHotelName() {
return hotelName;
}
public void setHotelName(String hotelName) {
this.hotelName = hotelName;
}
public String getHotelAddress() {
return hotelAddress;
}
public void setHotelAddress(String hotelAddress) {
this.hotelAddress = hotelAddress;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public City getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(City city) {
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hotel [id=" + id + ", hotelName=" + hotelName + ", hotelAddress=" + hotelAddress + ", price=" + price
+ "]";
}
}
增加城市类 City.java
package com.pjf.mybatis.po;
public class City {
private int cityCode;
private String cityName;
public int getCityCode() {
return cityCode;
}
public void setCityCode(int cityCode) {
this.cityCode = cityCode;
}
public String getCityName() {
return cityName;
}
public void setCityName(String cityName) {
this.cityName = cityName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "City [cityCode=" + cityCode + ", cityName=" + cityName + "]";
}
}
还有数据库的修改,hotel表中增加一列city_code,新增一个city表,
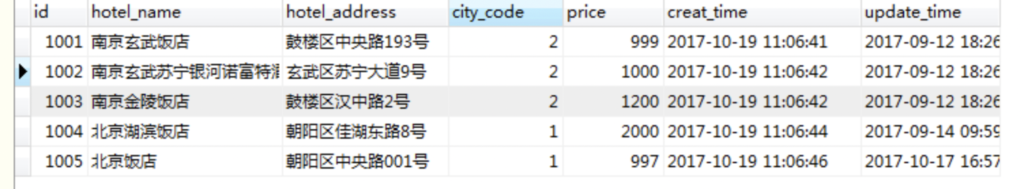
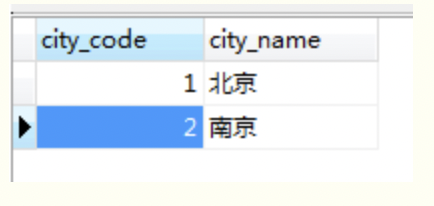
hotelMapper接口不变
package com.pjf.mybatis.dao;
import com.pjf.mybatis.po.Hotel;
public interface HotelMapper {
public Hotel getHotel(Integer i);
}
2、association的使用
通过association来关联city表,使用规则如下
hotelMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.pjf.mybatis.dao.HotelMapper">
<!-- resultMap定义 type:javaBean的全类名, id为该resultMap的唯一标识 -->
<resultMap type="com.pjf.mybatis.po.Hotel" id="myHotel">
<!--id 指定主键的封装规则 column:数据库中列名 property:javaBean的属性名 -->
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<!--result 指定非主键的封装规则 column:数据库中列名 property:javaBean的属性名 -->
<result column="hotel_name" property="hotelName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="hotel_address" property="hotelAddress"
jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="price" property="price" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<!--association 关联的表
property 指被关联的类成员变量
javaType 指被关联的类成员变量的全类名 -->
<association property="city" javaType="com.pjf.mybatis.po.City">
<id column="city_code" property="cityCode" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="city_name" property="cityName" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- resultMap使用 -->
<select id="getHotel" resultMap="myHotel">
select
h.id,h.hotel_name,h.hotel_address,h.price,c.city_code,c.city_name from
hotel h ,city c
where
h.city_code=c.city_code and h.id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
测试类:
package com.pjf.mybatis;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.pjf.mybatis.dao.HotelMapper;
import com.pjf.mybatis.po.Hotel;
public class TestHotel {
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "mybatis_config.xml";
// 使用类加载器加载mybatis的配置文件(它也加载关联的映射文件)TestHotel.class.getClassLoader()
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 构建sqlSession的工厂
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
return sessionFactory;
}
// 查
@Test
public void getHotel() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
HotelMapper hotelMapper = session.getMapper(HotelMapper.class);
System.out.println(hotelMapper.getClass());
Hotel hotel = hotelMapper.getHotel(1004);
// 打印酒店
System.out.println(hotel);
// 打印城市
System.out.println(hotel.getCity());
session.close();
}
}
这时候就可以看到结果了
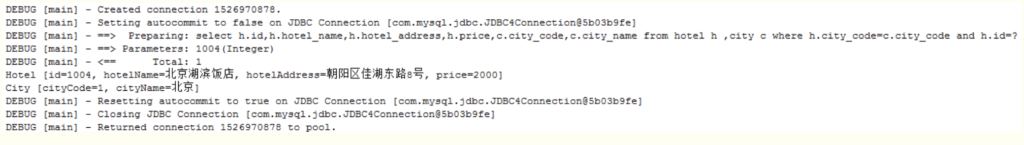
三、collection的使用
实例:查询某个城市的全部酒店
修改city类
package com.pjf.mybatis.po;
import java.util.List;
public class City {
private int cityCode;
private String cityName;
private List<Hotel> hotel;
public List<Hotel> getHotel() {
return hotel;
}
public void setHotel(List<Hotel> hotel) {
this.hotel = hotel;
}
public int getCityCode() {
return cityCode;
}
public void setCityCode(int cityCode) {
this.cityCode = cityCode;
}
public String getCityName() {
return cityName;
}
public void setCityName(String cityName) {
this.cityName = cityName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "City [cityCode=" + cityCode + ", cityName=" + cityName + "]";
}
}
修改hotelMapper接口(可以重新定义一个接口和mapper.xml文件)
package com.pjf.mybatis.dao;
import com.pjf.mybatis.po.City;
public interface HotelMapper {
public City getCityHotel(Integer i);
}
hotelMapper.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.pjf.mybatis.dao.HotelMapper">
<resultMap type="com.pjf.mybatis.po.City" id="cityHotel">
<id column="city_code" property="cityCode"/>
<result column="city_name" property="cityName"/>
<!--collection被关联的集合
ofType被关联集合元素的全类名
-->
<collection property="hotel" ofType="com.pjf.mybatis.po.Hotel">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="hotel_name" property="hotelName"/>
<result column="hotel_address" property="hotelAddress"/>
<result column="price" property="price"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getCityHotel" resultMap="cityHotel">
SELECT c.city_code,c.city_name ,h.id,h.hotel_name,h.hotel_address,h.price
FROM city c LEFT JOIN hotel h ON c.city_code=h.city_code
WHERE c.city_code=#{cityCode}
</select>
</mapper>
测试类
package com.pjf.mybatis;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.pjf.mybatis.dao.HotelMapper;
import com.pjf.mybatis.po.City;
import com.pjf.mybatis.po.Hotel;
public class TestHotel {
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "mybatis_config.xml";
// 使用类加载器加载mybatis的配置文件(它也加载关联的映射文件)TestHotel.class.getClassLoader()
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 构建sqlSession的工厂
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
return sessionFactory;
}
// 查
@Test
public void getHotel() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
HotelMapper hotelMapper = session.getMapper(HotelMapper.class);
System.out.println(hotelMapper.getClass());
City city = hotelMapper.getCityHotel(1);
// 打印城市
System.out.println(city);
// 打印酒店
for (Hotel hotel : city.getHotel()) {
System.out.println(hotel);
}
session.close();
}
}
查看结果
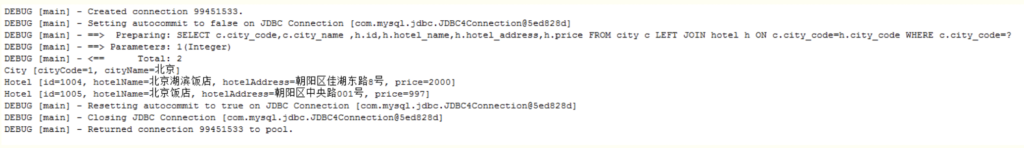
四、association 分步查询
场景:在实际的开发过程中,往往会从多个表里获取数据。此时需要用到多表操作。如查询用户的个人信息及部门信息。
实例:
UserMapper.java
public interface UserMapper {
UserInfo getUserInfoById (Integer id);
}
DepartmentMapper.java
public interface DepartmentMapper {
Department getDepartmentByUserId (Integer uid);
}
UserMapper.xml
<select id="getUserInfo" resultMap="userInfoMap">
SELECT username, age, workno, deptid
FROM user WHERE uid = #{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="userInfoMap" type="com.cat.pojo.UserInfo">
<result column="username" property="uname"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
<result column="workno" property="workNo"/>
<!-- 将查询出来的User对象的deptid传入,封装成具体的Department信息,得到用户的信息及Department信息 -->
<association property="dept" column="deptid" select="com.cat.mapper.DepartmentMapper.getDepartmentByUserId" />
</resultMap>
DepartmentMapper.xml
<select id="getDepartmentByUserId" parameterType="string" resultType="com.cat.pojo.Department">
SELECT department_name, leader FROM department WHERE id = #{deptId}
</select>
SQL执行过程:此时数据的查询将会分为两步,第一步将用户检索出来,第二步再根据每个用户的deptid查询到部门信息