在 WWDC 2021 上,苹果为开发者带来了有一个期待已久的功能——AttributedString,这意味着 Swift 开发人员不再需要使用基于 Objective-C 的 NSAttributedString 来创建样式化文本。本文将对其做全面的介绍并演示如何创建自定义属性。
初步印象
AttributedString 是具有单个字符或字符范围的属性的字符串。属性提供了一些特征,如用于显示的视觉风格、用于无障碍引导以及用于在数据源之间进行链接的超链接数据等。
下面的代码将生成一个包含粗体以及超链接的属性字符串。
var attributedString = AttributedString("请访问肘子的博客")
let zhouzi = attributedString.range(of: "肘子")! // 获取肘子二字的范围(Range)
attributedString[zhouzi].inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized // 设置属性——粗体
let blog = attributedString.range(of: "博客")!
attributedString[blog].link = URL(string: "https://www.fatbobman.com")! // 设置属性——超链接

在 WWDC 2021 之前,SwiftUI 没有提供对属性字符串的支持,如果我们希望显示具有丰富样式的文本,通常会采用以下三种方式:
- 将 UIKit 或 AppKit 控件包装成 SwiftUI 控件,在其中显示 NSAttributedString
- 通过代码将 NSAttributedString 转换成对应的 SwiftUI 布局代码
- 使用 SwiftUI 的原生控件组合显示
下面的文字随着 SwiftUI 版本的变化,可采取的手段也在不断地增加(不使用 NSAttributedString):

SwiftUI 1.0
@ViewBuilder
var helloView:some View{
HStack(alignment:.lastTextBaseline, spacing:0){
Text("Hello").font(.title).foregroundColor(.red)
Text(" world").font(.callout).foregroundColor(.cyan)
}
}
SwiftUI 2.0
SwiftUI 2.0 增强了 Text 的功能,我们可以将不同的 Text 通过+合并显示
var helloText:Text {
Text("Hello").font(.title).foregroundColor(.red) + Text(" world").font(.callout).foregroundColor(.cyan)
}
SwiftUI 3.0
除了上述的方法外,Text 添加了对 AttributedString 的原生支持
var helloAttributedString:AttributedString {
var hello = AttributedString("Hello")
hello.font = .title.bold()
hello.foregroundColor = .red
var world = AttributedString(" world")
world.font = .callout
world.foregroundColor = .cyan
return hello + world
}
Text(helloAttributedString)
单纯看上面的例子,并不能看到 AttributedString 有什么优势。相信随着继续阅读本文,你会发现 AttributedString 可以实现太多以前想做而无法做到的功能和效果。
AttributedString vs NSAttributedString
AttributedString 基本上可以看作是 NSAttributedString 的 Swift 实现,两者在功能和内在逻辑上差别不大。但由于形成年代、核心代码语言等,两者之间仍有不少的区别。本节将从多个方面对它们进行比较。
AttributedString 是值类型的,这也是它同由 Objective-C 构建的 NSAttributedString(引用类型)之间最大的区别。这意味着它可以通过 Swift 的值语义,像其他值一样被传递、复制和改变。
NSAttributedString 可变或不可变需不同的定义
let hello = NSMutableAttributedString("hello")
let world = NSAttributedString(" world")
hello.append(world)
AttributedString
var hello = AttributedString("hello")
let world = AttributedString(" world")
hello.append(world)
- 安全性
在 AttributedString 中需要使用 Swift 的点或键语法按名称访问属性,不仅可以保证类型安全,而且可以获得编译时检查的优势。
AttributedString 中基本不采用 NSAttributedString 如下的属性访问方式,极大的减少出错几率
// 可能出现类型不匹配
let attributes: [NSAttributedString.Key: Any] = [
.font: UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 72),
.foregroundColor: UIColor.white,
]
- 本地化支持
Attributed 提供了原生的本地化字符串支持,并可为本地化字符串添加了特定属性。
var localizableString = AttributedString(localized: "Hello \(Date.now,format: .dateTime) world",locale: Locale(identifier: "zh-cn"),option:.applyReplacementIndexAttribute)
- Formatter 支持
同为 WWDC 2021 中推出的新 Formatter API 全面支持了 AttributedString 类型的格式化输出。我们可以轻松实现过去无法完成的工作。
var dateString: AttributedString {
var attributedString = Date.now.formatted(.dateTime
.hour()
.minute()
.weekday()
.attributed
)
let weekContainer = AttributeContainer()
.dateField(.weekday)
let colorContainer = AttributeContainer()
.foregroundColor(.red)
attributedString.replaceAttributes(weekContainer, with: colorContainer)
return attributedString
}
Text(dateString)
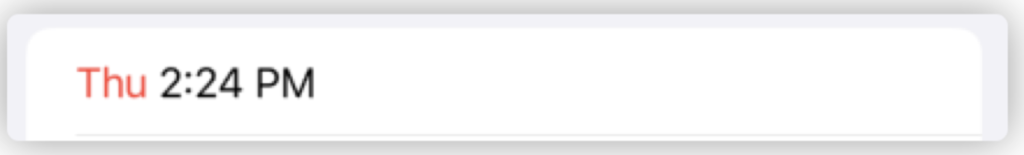
更多关于新 Formatter API 同 AttributedString 配合范例,请参阅 WWDC 2021 新 Formatter API:新老比较及如何自定义
- SwiftUI 集成
SwiftUI 的 Text 组件提供了对 AttributedString 的原生支持,改善了一个 SwiftUI 的长期痛点(不过 TextField、TextEdit 仍不支持)。
AttributedString 同时提供了 SwiftUI、UIKit、AppKit 三种框架的可用属性。UIKit 或 AppKit 的控件同样可以渲染 AttributedString(需经过转换)。
- 支持的文件格式
AttributedString 目前仅具备对 Markdown 格式文本进行解析的能力。同 NSAttributedString 支持 Markdown、rtf、doc、HTML 相比仍有很大差距。
- 转换
苹果为 AttributedString 和 NSAttributedString 提供了相互转换的能力。
// AttributedString -> NSAttributedString
let nsString = NSMutableAttributedString("hello")
var attributedString = AttributedString(nsString)
// NSAttribuedString -> AttributedString
var attString = AttributedString("hello")
attString.uiKit.foregroundColor = .red
let nsString1 = NSAttributedString(attString)
开发者可以充分利用两者各自的优势进行开发。比如:
- 用 NSAttributedString 解析 HTML,然后转换成 AttributedString 调用
- 用 AttributedString 创建类型安全的字符串,在显示时转换成 NSAttributedString
基础
本节中,我们将对 AttributedString 中的一些重要概念做介绍,并通过代码片段展示 AttributedString 更多的用法。
- AttributedStringKey
AttributedStringKey 定义了 AttributedString 属性名称和类型。通过点语法或 KeyPath,在保证类型安全的前提进行快捷访问。
var string = AttributedString("hello world")
// 使用点语法
string.font = .callout
let font = string.font
// 使用 KeyPath
let font = string[keyPath:\.font]
除了使用系统预置的大量属性外,我们也可以创建自己的属性。例如:
enum OutlineColorAttribute : AttributedStringKey {
typealias Value = Color // 属性类型
static let name = "OutlineColor" // 属性名称
}
string.outlineColor = .blue
我们可以使用点语法或 KeyPath 对 AttributedString、AttributedSubString、AttributeContainer 以及 AttributedString.Runs.Run 的属性进行访问。更多用法参照本文其他的代码片段。
- AttributeContainer
AttributeContainer 是属性容器。通过配置 container,我们可以一次性地为属性字符串(或片段)设置、替换、合并大量的属性。
设置属性
var attributedString = AttributedString("Swift")
string.foregroundColor = .red
var container = AttributeContainer()
container.inlinePresentationIntent = .strikethrough
container.font = .caption
container.backgroundColor = .pink
container.foregroundColor = .green //将覆盖原来的 red
attributedString.setAttributes(container) // attributdString 此时拥有四个属性内容
替换属性
var container = AttributeContainer() container.inlinePresentationIntent = .strikethrough container.font = .caption container.backgroundColor = .pink container.foregroundColor = .green attributedString.setAttributes(container) // 此时 attributedString 有四个属性内容 font、backgroundColor、foregroundColor、inlinePresentationIntent // 被替换的属性 var container1 = AttributeContainer() container1.foregroundColor = .green container1.font = .caption // 将要替换的属性 var container2 = AttributeContainer() container2.link = URL(string: "https://www.swift.org") // 被替换属性 contianer1 的属性键值内容全部符合才可替换,比如 continaer1 的 foregroundColor 为。red 将不进行替换 attributedString.replaceAttributes(container1, with: container2) // 替换后 attributedString 有三个属性内容 backgroundColor、inlinePresentationIntent、link
合并属性
var container = AttributeContainer() container.inlinePresentationIntent = .strikethrough container.font = .caption container.backgroundColor = .pink container.foregroundColor = .green attributedString.setAttributes(container) // 此时 attributedString 有四个属性内容 font、backgroundColor、foregroundColor、inlinePresentationIntent var container2 = AttributeContainer() container2.foregroundColor = .red container2.link = URL(string: "www.swift.org") attributedString.mergeAttributes(container2,mergePolicy: .keepNew) // 合并后 attributedString 有五个属性 ,font、backgroundColor、foregroundColor、inlinePresentationIntent 及 link // foreground 为。red // 属性冲突时,通过 mergePolicy 选择合并策略 .keepNew(默认) 或 .keepCurrent
- AttributeScope
属性范围是系统框架定义的属性集合,将适合某个特定域中的属性定义在一个范围内,一方面便于管理,另一方面也解决了不同框架下相同属性名称对应类型不一致的问题。
目前,AttributedString 提供了 5 个预置的 Scope,分别为
- foundation
包含有关 Formatter、Markdown、URL 以及语言变形方面的属性
- swiftUI
可以在 SwiftUI 下被渲染的属性,例如 foregroundColor、backgroundColor、font 等。目前支持的属性明显少于 uiKit 和 appKit。估计待日后 SwiftUI 提供更多的显示支持后会逐步补上其他暂不支持的属性。
- uiKit
可以在 UIKit 下被渲染的属性。
- appKit
可以在 AppKit 下被渲染的属性
- accessibility
适用于无障碍的属性,用于提高引导访问的可用性。
在 swiftUI、uiKit 和 appKit 三个 scope 中存在很多的同名属性(比如 foregroundColor),在访问时需注意以下几点:
- 当 Xcode 无法正确推断该适用哪个 Scope 中的属性时,请显式标明对应的 AttributeScope
uiKitString.uiKit.foregroundColor = .red //UIColor appKitString.appKit.backgroundColor = .yellow //NSColor
- 三个框架的同名属性并不能互转,如想字符串同时支持多框架显示(代码复用),请分别为不同 Scope 的同名属性赋值
attributedString.swiftUI.foregroundColor = .red attributedString.uiKit.foregroundColor = .red attributedString.appKit.foregroundColor = .red // 转换成 NSAttributedString,可以只转换指定的 Scope 属性 let nsString = try! NSAttributedString(attributedString, including: \.uiKit)
- 为了提高兼容性,部分功能相同的属性,可以在 foundation 中设置。
attributedString.inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized //相当于 bold
- swiftUI、uiKit 和 appKit 三个 Scope 在定义时,都已经分别包含了 foundation 和 accessibility。因此在转换时即使只指定单一框架,foundation 和 accessibility 的属性也均可正常转换。我们在自定义 Scope 时,最好也遵守该原则。
let nsString = try! NSAttributedString(attributedString, including: \.appKit) // attributedString 中属于 foundation 和 accessibility 的属性也将一并被转换
- 视图
在属性字符串中,属性和文本可以被独立访问,AttributedString 提供了三种视图方便开发者从另一个维度访问所需的内容。
Character 和 unicodeScalar 视图
这两个视图提供了类似 NSAttributedString 的 string 属性的功能,让开发者可以在纯文本的维度操作数据。两个视图的唯一区别是类型不同,简单来说,你可以把 ChareacterView 看作是 Charecter 集合,而 UnicodeScalarView 看作是 Unicode 标量合集。
字符串长度
var attributedString = AttributedString("Swift")
attributedString.characters.count // 5
长度 2
let attributedString = AttributedString("hello 👩🏽🦳")
attributedString.characters.count // 7
attributedString.unicodeScalars.count // 10
转换成字符串
String(attributedString.characters) // "Swift"
替换字符串
var attributedString = AttributedString("hello world")
let range = attributedString.range(of: "hello")!
attributedString.characters.replaceSubrange(range, with: "good")
// good world , 替换后的 good 仍会保留 hello 所在位置的所有属性
- Runs 视图
AttributedString 的属性视图。每个 Run 对应一个属性完全一致的字符串片段。用 for-in 语法来迭代 AttributedString 的 runs 属性。
只有一个 Run
整个属性字符串中所有的字符属性都一致
let attributedString = AttribuedString("Core Data")
print(attributedString)
// Core Data {}
print(attributedString.runs.count) // 1
两个 Run
属性字符串coreData,Core和 Data两个片段的属性不相同,因此产生了两个 Run
var coreData = AttributedString("Core")
coreData.font = .title
coreData.foregroundColor = .green
coreData.append(AttributedString(" Data"))
for run in coreData.runs { //runs.count = 2
print(run)
}
// Core {
// SwiftUI.Font = Font(provider: SwiftUI.(unknown context at $7fff5cd3a0a0).FontBox<SwiftUI.Font.(unknown context at $7fff5cd66db0).TextStyleProvider>)
// SwiftUI.ForegroundColor = green
// }
// Data {}
多个 Run
var multiRunString = AttributedString("The attributed runs of the attributed string, as a view into the underlying string.")
while let range = multiRunString.range(of: "attributed") {
multiRunString.characters.replaceSubrange(range, with: "attributed".uppercased())
multiRunString[range].inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized
}
var n = 0
for run in multiRunString.runs {
n += 1
}
// n = 5
最终结果:The ATTRIBUTED runs of the ATTRIBUTED string, as a view into the underlying string.
利用 Run 的 range 进行属性设置
// 继续使用上文的 multiRunString
// 将所有非强调字符设置为黄色
for run in multiRunString.runs {
guard run.inlinePresentationIntent != .stronglyEmphasized else {continue}
multiRunString[run.range].foregroundColor = .yellow
}
通过 Runs 获取指定的属性
// 将颜色为黄色且为粗体的文字改成红色
for (color,intent,range) in multiRunString.runs[\.foregroundColor,\.inlinePresentationIntent] {
if color == .yellow && intent == .stronglyEmphasized {
multiRunString[range].foregroundColor = .red
}
}
通过 Run 的 attributes 收集所有使用到的属性
var totalKeysContainer = AttributeContainer()
for run in multiRunString.runs{
let container = run.attributes
totalKeysContainer.merge(container)
}
使用 Runs 视图可以方便的从众多属性中获取到需要的信息
不使用 Runs 视图,达到类似的效果
multiRunString.transformingAttributes(\.foregroundColor,\.font){ color,font in
if color.value == .yellow && font.value == .title {
multiRunString[color.range].backgroundColor = .green
}
}
尽管没有直接调用 Runs 视图,不过 transformingAttributes 闭包的调用时机同 Runs 的时机是一致的。transformingAttributes 最多支持获取 5 个属性。
- Range
在本文之前的代码中,已经多次使用过 Range 来对属性字符串的内容进行访问或修改。
对属性字符串中局部内容的属性进行修改可以使用两种方式:
- 通过 Range
- 通过 AttributedContainer
通过关键字获取 Range
// 从属性字符串的结尾向前查找,返回第一个满足关键字的 range(忽略大小写)
if let range = multiRunString.range(of: "Attributed", options: [.backwards, .caseInsensitive]) {
multiRunString[range].link = URL(string: "https://www.apple.com")
}
使用 Runs 或 transformingAttributes 获取 Range
之前的例子中已反复使用
通过本文视图获取 Range
if let lowBound = multiRunString.characters.firstIndex(of: "r"),
let upperBound = multiRunString.characters.firstIndex(of: ","),
lowBound < upperBound
{
multiRunString[lowBound...upperBound].foregroundColor = .brown
}
本地化
创建本地化属性字符串
// Localizable Chinese "hello" = "你好"; // Localizable English "hello" = "hello"; let attributedString = AttributedString(localized: "hello")
在英文和中文环境中,将分别显示为hello 和 你好
目前本地化的 AttributedString 只能显示为当前系统设置的语言,并不能指定成某个特定的语言
var hello = AttributedString(localized: "hello")
if let range = hello.range(of: "h") {
hello[range].foregroundColor = .red
}
本地化字符串的文字内容将随系统语言而变化,上面的代码在中文环境下将无法获取到 range。需针对不同的语言做调整。
replacementIndex
可以为本地化字符串的插值内容设定 index(通过applyReplacementIndexAttribute), 方便在本地化内容中查找
// Localizable Chinese
"world %@ %@" = "%@ 世界 %@";
// Localizable English
"world %@ %@" = "world %@ %@";
var world = AttributedString(localized: "world \("👍") \("🥩")",options: .applyReplacementIndexAttribute) // 创建属性字符串时,将按照插值顺序设定 index ,👍 index == 1 🥩 index == 2
for (index,range) in world.runs[\.replacementIndex] {
switch index {
case 1:
world[range].baselineOffset = 20
world[range].font = .title
case 2:
world[range].backgroundColor = .blue
default:
world[range].inlinePresentationIntent = .strikethrough
}
}
在中文和英文环境中,分别为:
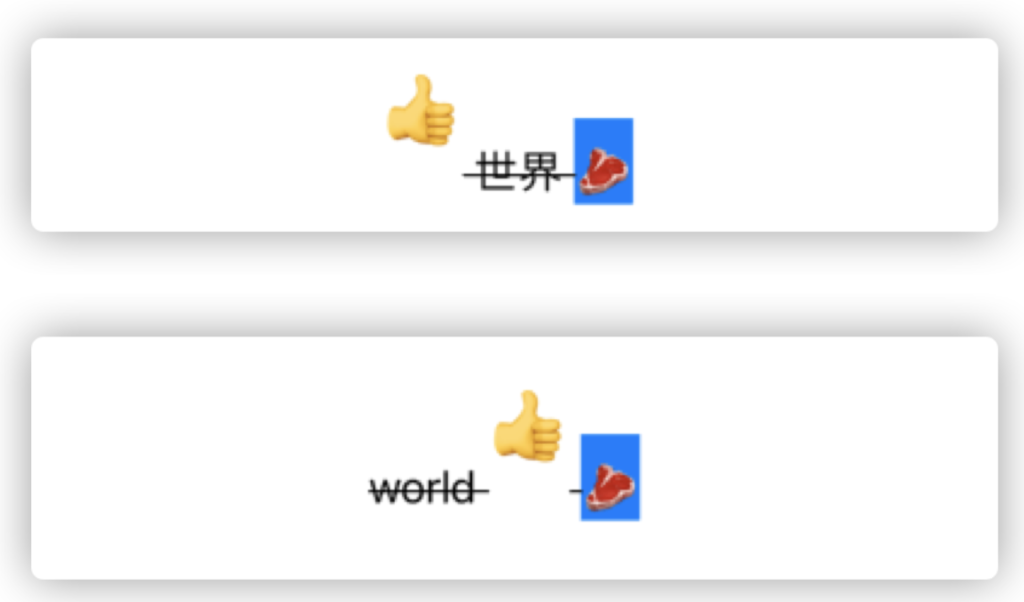
使用 locale 设定字符串插值中的 Formatter
AttributedString(localized: "\(Date.now, format: Date.FormatStyle(date: .long))", locale: Locale(identifier: "zh-cn")) // 即使在英文环境中也会显示 2021 年 10 月 7 日
用 Formatter 生成属性字符串
var dateString = Date.now.formatted(.dateTime.year().month().day().attributed)
dateString.transformingAttributes(\.dateField) { dateField in
switch dateField.value {
case .month:
dateString[dateField.range].foregroundColor = .red
case .day:
dateString[dateField.range].foregroundColor = .green
case .year:
dateString[dateField.range].foregroundColor = .blue
default:
break
}
}

Markdown 符号
从 SwiftUI 3.0 开始,Text 已经对部分 Markdown 标签提供了支持。在本地化的属性字符串中,也提供了类似的功能,并且会在字符串中设置对应的属性。提供了更高的灵活性。
var markdownString = AttributedString(localized: "**Hello** ~world~ _!_")
for (inlineIntent,range) in markdownString.runs[\.inlinePresentationIntent] {
guard let inlineIntent = inlineIntent else {continue}
switch inlineIntent{
case .stronglyEmphasized:
markdownString[range].foregroundColor = .red
case .emphasized:
markdownString[range].foregroundColor = .green
case .strikethrough:
markdownString[range].foregroundColor = .blue
default:
break
}
}
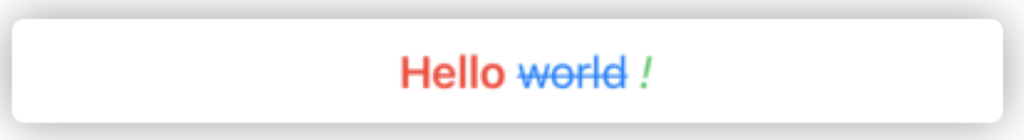
Markdown 解析
AttributedString 不仅可以在本地化字符串中支持部分的 Markdown 标签,并且提供了一个完整的 Markdown 解析器。
支持从 String、Data 或 URL 中解析 Markdown 文本内容。
比如:
let mdString = try! AttributedString(markdown: "# Title\n**hello**\n")
print(mdString)
// 解析结果
Title {
NSPresentationIntent = [header 1 (id 1)]
}
hello {
NSInlinePresentationIntent = NSInlinePresentationIntent(rawValue: 2)
NSPresentationIntent = [paragraph (id 2)]
}
解析后会将文字风格和标签设置在inlinePresentationIntent和presentationIntent中。
- inlinePresentationIntent
字符性质:比如粗体、斜体、代码、引用等
- presentationIntent
段落属性:比如段落、表格、列表等。一个 Run 中,presentationIntent 可能会有多个内容,用 component 来获取。
README.md
# Hello
## Header2
hello **world**
* first
* second
> test `print("hello world")`
| row1 | row2 |
| ---- | ---- |
| 34 | 135 |
[新 Formatter 介绍](/posts/newFormatter/)
解析代码:
let url = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "README", withExtension: "md")! var markdownString = try! AttributedString(contentsOf: url,baseURL: URL(string: "https://www.fatbobman.com"))
解析后结果(节选):
Hello {
NSPresentationIntent = [header 1 (id 1)]
}
Header2 {
NSPresentationIntent = [header 2 (id 2)]
}
first {
NSPresentationIntent = [paragraph (id 6), listItem 1 (id 5), unorderedList (id 4)]
}
test {
NSPresentationIntent = [paragraph (id 10), blockQuote (id 9)]
}
print("hello world") {
NSPresentationIntent = [paragraph (id 10), blockQuote (id 9)]
NSInlinePresentationIntent = NSInlinePresentationIntent(rawValue: 4)
}
row1 {
NSPresentationIntent = [tableCell 0 (id 13), tableHeaderRow (id 12), table [Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn(alignment: Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn.Alignment.left), Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn(alignment: Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn.Alignment.left)] (id 11)]
}
row2 {
NSPresentationIntent = [tableCell 1 (id 14), tableHeaderRow (id 12), table [Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn(alignment: Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn.Alignment.left), Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn(alignment: Foundation.PresentationIntent.TableColumn.Alignment.left)] (id 11)]
}
新 Formatter 介绍 {
NSPresentationIntent = [paragraph (id 18)]
NSLink = /posts/newFormatter/ -- https://www.fatbobman.com
}
解析后的内容包括段落属性、标题号、表格列数、行数、对齐方式等。缩紧、标号等其他信息可以在代码中可以通过枚举关联值来处理。
大致的代码如下:
for run in markdownString.runs {
if let inlinePresentationIntent = run.inlinePresentationIntent {
switch inlinePresentationIntent {
case .strikethrough:
print("删除线")
case .stronglyEmphasized:
print("粗体")
default:
break
}
}
if let presentationIntent = run.presentationIntent {
for component in presentationIntent.components {
switch component.kind{
case .codeBlock(let languageHint):
print(languageHint)
case .header(let level):
print(level)
case .paragraph:
let paragraphID = component.identity
default:
break
}
}
}
}
SwiftUI 并不支持 presentationIntent 附加信息的渲染。如果想获得理想的显示效果,请自行编写视觉风格设置代码。
自定义属性
使用自定义属性,不仅有利于开发者创建更符合自身要求的属性字符串,而且通过在 Markdown 文本中添加自定义属性信息,进一步降低信息和代码的耦合度,提高灵活度。
自定义属性的基本流程为:
- 创建自定义 AttributedStringKey
为每个需要添加的属性创建一个符合 Attributed 协议的数据类型。
- 创建自定义 AttributeScope 并扩展 AttributeScopes
创建自己的 Scope,并在其中添加所有的自定义属性。为了方便自定义属性集被用于需要指定 Scope 的场合,在自定义 Scope 中推荐嵌套入需要的系统框架 Scope(swiftUI、uiKit、appKit)。并在 AttributeScopes 中添加上自定义的 Scope。
- 扩展 AttributeDynamicLookup(支持点语法)
在 AttributeDynamicLookup 中创建符合自定义 Scope 的下标方法。为点语法、KeyPath 提供动态支持。
实例 1:创建 id 属性
本例中我们将创建一个名称为 id 的属性。
struct MyIDKey:AttributedStringKey {
typealias Value = Int // 属性内容的类型。类型需要符合 Hashable
static var name: String = "id" // 属性字符串内部保存的名称
}
extension AttributeScopes{
public struct MyScope:AttributeScope{
let id:MyIDKey // 点语法调用的名称
let swiftUI:SwiftUIAttributes // 在我的 Scope 中将系统框架 swiftUI 也添加进来
}
var myScope:MyScope.Type{
MyScope.self
}
}
extension AttributeDynamicLookup{
subscript<T>(dynamicMember keyPath:KeyPath<AttributeScopes.MyScope,T>) -> T where T:AttributedStringKey {
self[T.self]
}
}
调用
var attribtedString = AttributedString("hello world")
attribtedString.id = 34
print(attribtedString)
// Output
hello world {
id = 34
}
实例 2:创建枚举属性,并支持 Markdown 解析
如果我们希望自己创建的属性可以在 Markdown 文本中被解析,需要让自定义的属性符合CodeableAttributedStringKey以及MarkdownDecodableAttributedStringKye
// 自定义属性的数据类型不限,只要满足需要的协议即可
enum PriorityKey:CodableAttributedStringKey,MarkdownDecodableAttributedStringKey{
public enum Priority:String,Codable{ //如需在 Markdown 中解析,需要将 raw 类型设置为 String, 并符合 Codable
case low
case normal
case high
}
static var name: String = "priority"
typealias Value = Priority
}
extension AttributeScopes{
public struct MyScope:AttributeScope{
let id:MyIDKey
let priority:PriorityKey // 将新创建的 Key 也添加到自定义的 Scope 中
let swiftUI:SwiftUIAttributes
}
var myScope:MyScope.Type{
MyScope.self
}
}
在 Markdown 中使用
^[text](属性名称:属性值)来标记自定义属性
调用
// 在 Markdown 文本中解析自定义属性时,需指明 Scope。
var attributedString = AttributedString(localized: "^[hello world](priority:'low')",including: \.myScope)
print(attributedString)
// Output
hello world {
priority = low
NSLanguage = en
}
实例 3:创建多参数的属性
enum SizeKey:CodableAttributedStringKey,MarkdownDecodableAttributedStringKey{
public struct Size:Codable,Hashable{
let width:Double
let height:Double
}
static var name: String = "size"
typealias Value = Size
}
// 在 Scope 中添加
let size:SizeKey
调用
// 多参数在{}内添加
let attributedString = AttributedString(localized: "^[hello world](size:{width:343.3,height:200.3},priority:'high')",including: \.myScope)
print(attributedString)
// Output
ello world {
priority = high
size = Size(width: 343.3, height: 200.3)
NSLanguage = en
}
在 WWDC 2021 新 Formatter API 一文中,还有在 Formatter 中使用自定义属性的案例
总结
在 AttributedString 之前,多数开发者将属性字符串主要用于文本的显示样式描述,随着可以在 Markdown 文本中添加自定义属性,相信很快就会有开发者扩展 AttributedString 的用途,将其应用到更多的场景中。
希望本文能够对你有所帮助。