今天分享一个Java开发中经常遇到的问题:拷贝对象时,有时候改了一个对象,另一个对象也跟着变了。这是怎么回事呢?
其实这涉及到拷贝的两种方式:浅拷贝和深拷贝。别被名字吓到,一个例子就能搞懂!
什么是浅拷贝?
只复制对象的表面,内部引用还是共享的
我们先看一个简单的例子:
public classStudent {
private String name;
private List<String> hobbies;
// 构造方法、getter、setter省略...
// 浅拷贝方法
public Student shallowCopy() {
Studentcopy=newStudent();
copy.name = this.name;
copy.hobbies = this.hobbies; // 直接赋值引用
return copy;
}
}
测试一下:
public classTest {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) {
Studentstudent1=newStudent();
student1.setName("小明");
student1.setHobbies(Arrays.asList("篮球", "游戏"));
// 浅拷贝
Studentstudent2= student1.shallowCopy();
// 修改student2的爱好
student2.getHobbies().add("编程");
System.out.println("student1的爱好:" + student1.getHobbies());
System.out.println("student2的爱好:" + student2.getHobbies());
}
}
输出结果:
student1的爱好:[篮球, 游戏, 编程] student2的爱好:[篮球, 游戏, 编程]
看到了吗?我们只修改了student2,但student1也跟着变了!这就是浅拷贝的特点。
什么是深拷贝?
不仅复制对象表面,连内部的引用对象也重新创建
再看深拷贝的实现:
public classStudent {
private String name;
private List<String> hobbies;
// 深拷贝方法
public Student deepCopy() {
Studentcopy=newStudent();
copy.name = this.name;
copy.hobbies = newArrayList<>(this.hobbies); // 创建新的List
return copy;
}
}
测试深拷贝:
public classTest {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) {
Studentstudent1=newStudent();
student1.setName("小明");
student1.setHobbies(Arrays.asList("篮球", "游戏"));
// 深拷贝
Studentstudent3= student1.deepCopy();
// 修改student3的爱好
student3.getHobbies().add("编程");
System.out.println("student1的爱好:" + student1.getHobbies());
System.out.println("student3的爱好:" + student3.getHobbies());
}
}
输出结果:
student1的爱好:[篮球, 游戏] student3的爱好:[篮球, 游戏, 编程]
这次student1没有受到影响,这就是深拷贝的效果!
两者区别一目了然
通过内存结构图理解本质差异
让我们用图来看看内存中发生了什么:
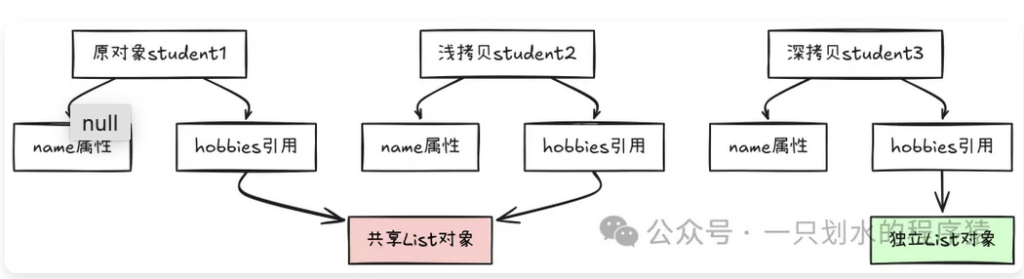
浅拷贝的问题:两个对象的hobbies引用指向同一个List,修改任何一个都会影响另一个。
深拷贝的优势:每个对象都有自己独立的List,互不影响。
开发中的实际应用
知道什么时候该用哪种拷贝
1. 配置对象拷贝
// 系统配置需要深拷贝,避免误修改影响全局 SystemConfig backupConfig = originalConfig.deepCopy();
2. 缓存数据拷贝
// 从缓存取出的对象要深拷贝,避免业务修改污染缓存 User userFromCache = cache.get(userId).deepCopy();
3. 什么时候用浅拷贝
// 只是想复制基本属性,内部对象本身就是不可变的 Student student = original.shallowCopy(); // String是不可变的,可以放心浅拷贝
实现深拷贝的常用方法
三种方式,各有特点
方法一:手动实现
public Student deepCopy() {
Student copy = new Student();
copy.name = this.name;
copy.hobbies = new ArrayList<>(this.hobbies);
return copy;
}
方法二:使用序列化
// 需要实现Serializable接口
public Student deepCopy()throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStreambos=newByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStreamoos=newObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
ByteArrayInputStreambis=newByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStreamois=newObjectInputStream(bis);
return (Student) ois.readObject();
}
方法三:使用工具库
// 使用Apache Commons Lang Student copy = SerializationUtils.clone(original); // 使用JSON转换(需要Gson等库) String json = gson.toJson(original); Student copy = gson.fromJson(json, Student.class);
总结
记住这个口诀:
- • 浅拷贝:表面兄弟,内心相通
- • 深拷贝:独立个体,各自精彩
在实际开发中,大部分情况下我们需要的是深拷贝,特别是涉及到集合、数组等引用类型的时候。